Your gift is 100% tax deductible.
If You Have a Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumor
Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors are a type of cancer in the lining of the digestive tract (the gut). Cancer starts when cells begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer. To learn more about what cancer is and how it can grow and spread, see What Is Cancer?
- What is a gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumor (GI NET)?
- Neuroendocrine tumors
- How will the doctor know if I have a GI neuroendocrine tumor?
- Signs and symptoms from hormones made by neuroendocrine tumors
- Tests that may be done
- How serious is my cancer?
- What kind of treatment will I need?
- What will happen after treatment?
What is a gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumor (GI NET)?
To understand gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors, it helps to know about the digestive system, as well as the neuroendocrine system.
The gastrointestinal system
The gastrointestinal (GI) system, also known as the digestive system, turns food into energy and rids the body of solid waste. After food is chewed and swallowed, it enters the esophagus. This tube carries food through the neck and chest to the stomach. The esophagus joins the stomach (a sac that holds food and begins the digestive process by secreting gastric juice). The food and gastric juices are mixed into a thick fluid, which then empties into the small intestine.
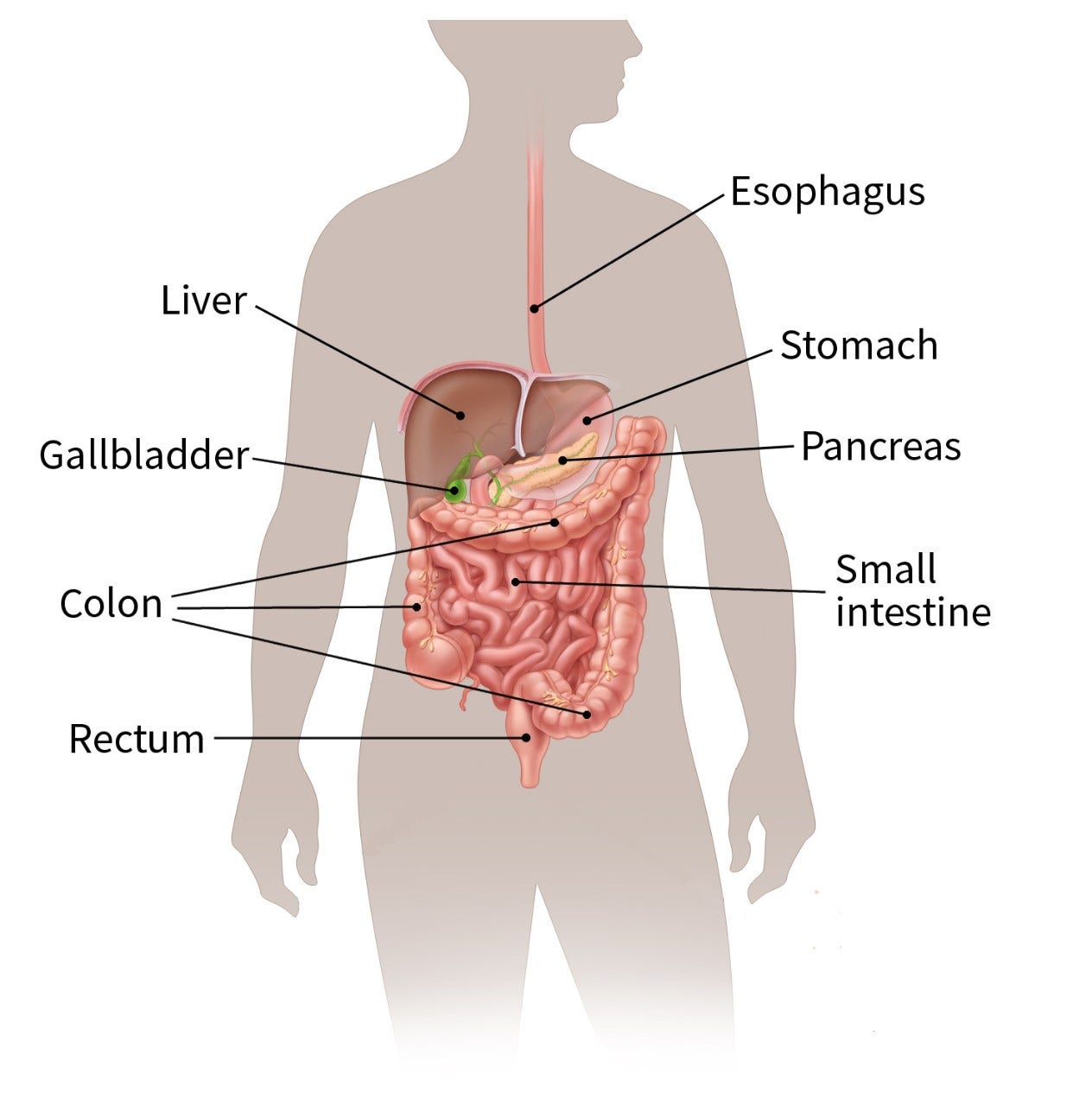
The small intestine continues breaking down food and absorbs most of the nutrients. It is the longest section of the gut, measuring more than 20 feet. The small intestine then joins the colon, which is a wider tube about 5 feet long. The appendix is found near the corner of the small intestine and colon. The colon absorbs water and nutrients from food and stores the waste. The waste that is left goes into the rectum. From there, it passes out of the body through the anus as stool (feces).
The neuroendocrine system
This system is made up of cells that are like nerve cells in certain ways and like hormone-making cells in other ways. These cells do not form an organ like the adrenal or thyroid glands. Instead, they are scattered throughout the body in organs like the lungs, stomach, and intestines. Neuroendocrine tumors start from cells of the neuroendocrine system.
Neuroendocrine cells help control the release of digestive juices and how fast food moves in the gut. They may also help control the growth of other types of digestive system cells.
Neuroendocrine tumors
Like most cells in the body, neuroendocrine cells in the gut sometimes have certain changes that cause them to grow too much and form tumors.
- Neuroendocrine tumors are growths that look benign but can possibly spread to other parts of the body.
- Low-grade (grade 1) tumors have cells that do not look very abnormal and grow slowly.
- Intermediate-grade (grade 2) tumors look in between those of low and high-grade tumors.
- Neuroendocrine cancers can spread to other parts of the body. They are called high-grade (grade 3) cancers because the cells look very abnormal and are growing quickly.
Questions to ask the doctor
- Can you please write down the type of cancer that I have?
- Why do you think I might have a GI neuroendocrine tumor?
- Could my symptoms be caused by something else?
- What will happen next?
How will the doctor know if I have a GI neuroendocrine tumor?
The symptoms a person can have from a GI neuroendocrine tumor often depend on where it is growing.
The appendix
People with appendix tumors often don’t have symptoms. If a tumor is found, it is usually when an appendix is removed during an operation for another problem. Sometimes, the tumor blocks the opening between the appendix and the rest of the intestine and causes appendicitis. This can lead to symptoms like fever, nausea, vomiting, and belly pain.
The small intestine or colon
If the tumor starts in the small intestine, it can cause the intestines (bowel) to kink and be blocked for a while. This can cause cramps, belly pain, weight loss, fatigue, bloating, diarrhea, or nausea and vomiting, which might come and go. This can sometimes go on for years before the tumor is found. A tumor usually needs to grow large before it completely blocks the bowel and causes a possible life-threatening condition.
The rectum
Rectal neuroendocrine tumors are often found during routine exams, even though they can cause pain and bleeding from the rectum and constipation.
The stomach
Neuroendocrine tumors that start in the stomach usually grow slowly and often do not cause symptoms. They are sometimes found when the stomach is examined for other conditions.
Signs and symptoms from hormones made by neuroendocrine tumors
Some neuroendocrine tumors can release enough hormone-like substances into the blood to cause the symptoms of carcinoid syndrome. These include:
- Facial flushing (redness and warm feeling)
- Severe diarrhea
- Wheezing
- Fast heartbeat
Many people find that stress, heavy exercise, and drinking alcohol can also trigger these symptoms. Over time, these hormone-like substances can damage the heart, causing shortness of breath, weakness, and a heart murmur (an abnormal heart sound).
Not all GI neuroendocrine tumors cause carcinoid syndrome. Most cases of carcinoid syndrome develop only after the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, like the liver.
Tests that may be done
Barium x-ray: These tests use barium (a chalky white liquid) to coat the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. The coating helps show abnormal areas in these organs.
CT or CT scan: Uses x-rays to make pictures of your insides. This can show clear pictures of the abdomen and the area around it to see if the cancer has spread. CT scans can also be used to do a biopsy (see below).
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan: Uses radio waves and strong magnets instead of x-rays to make clear pictures of the inside of the body. MRI scans help look at the liver.
PET scan: PET scans use a kind of sugar that can be seen inside your body with a special camera. If there is cancer, the sugar shows up as “hot spots” where the cancer is found. This test is useful when your doctor thinks the cancer has spread but doesn’t know where. For GI neuroendocrine tumors, a different substance is used instead of sugar to find the cancer cells.
Octreotide scan: Octreotide is a hormone-like substance that attaches to neuroendocrine cells. A small amount of octreotide with a radioactive substance is injected into your veins. It travels through the blood and attaches to carcinoid tumors. A few hours after the injection, a special camera will show where the radioactivity has collected in the body showing where the tumors are located.
Biopsy: For a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of the tumor. It’s sent to the lab to see if it has cancer cells. This is the best way to know for sure if you have cancer.
Blood/urine tests: Blood/urine tests are not used to find GI neuroendocrine tumors, but they are done to tell the doctor more about your health.
Questions to ask the doctor
- What tests will I need to have?
- Who will do these tests?
- Where will they be done?
- How and when will I get the results?
- Who will explain the results to me?
- What do I need to do next?
How serious is my cancer?
If you have a GI neuroendocrine tumor, the doctor will want to find out if and how far it has spread. This is called staging. Knowing the cancer's stage helps your doctor decide what treatment is best for you.
For most GI neuroendocrine tumors, the stage describes the growth of the cancer through the layers of the wall of the digestive system. It also tells if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or to organs like the liver.
Be sure to ask your doctor about the stage of your cancer and what it might mean for you.
Questions to ask the doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- Can all my cancer be removed with surgery?
- What will happen next?
What kind of treatment will I need?
The treatment plan that is best for you depends on the stage of your cancer, your age and overall health, the possibility the cancer can be removed with surgery, and other factors. Often, treatment helps make symptoms better and slows down the cancer, but might not cure it. Talk with your doctor to find out your options.
Surgery
Surgery is the main treatment for GI neuroendocrine tumors. If the tumor hasn’t spread, it can often be cured by surgery alone. Sometimes, part of the organ (like the stomach or intestine) must be removed along with nearby lymph nodes.
Side effects of surgery
Any type of surgery can have risks and side effects. Ask the doctor what you can expect. If you have problems, let your doctors know.
Tumor ablation for liver cancer
Tumor ablation destroys the tumor without taking it out. There are a few ways to do this, such as heating the tumor, freezing the tumor, or killing the tumor by putting alcohol in it. Ask the doctor about the planned treatment and what you can expect.
Radiation treatment
Radiation uses high-energy rays (such as x-rays) to kill cancer cells. It may be an option for those who can’t have surgery, and it may also be given after surgery in some cases if there’s a chance some of the tumor was not removed. Radiation can also be used to ease some problems caused by the cancer. It’s given in small doses every day for many weeks.
Side effects of radiation treatments
If your doctor suggests radiation as your treatment, ask what side effects might happen. They can include:
- Skin changes where the radiation is given
- Feeling very tired (fatigue)
- Feeling sick to your stomach
- Diarrhea
Most side effects get better after treatment ends. Some might last longer. Talk to your doctor about what you can expect.
Chemo
Chemo (the short word for chemotherapy) is the use of drugs to fight cancer. Chemo drugs can be used together or alone, and often with other types of medicines. Treatment often lasts for many months.
Most neuroendocrine tumors are not treated with chemo. It is mainly used for tumors that have spread to other organs, are causing severe symptoms, have not gotten smaller with other medicines, or tumors that are growing quickly.
The drugs may be given through a needle into a vein or taken as pills. These drugs go into the blood and spread through the body.
Chemo is given in cycles or rounds. There’s often a rest period after each treatment. This gives the body time to get better from any side effects.
Side effects of chemo
Chemo can have many side effects, like:
- Hair loss
- Mouth sores
- Not feeling like eating
- Diarrhea
- Feeling sick to your stomach
- More risk of infections
- Bruising and bleeding easily
- Tiredness
These problems tend to go away after treatment ends, but there are ways to treat most side effects. Be sure to talk to your cancer care team so they can help.
Radioactive drugs
Drugs containing radioactive particles may be used to treat some neuroendocrine tumors. This type of treatment lets doctors deliver high doses of radiation directly to the tumors.
The most common side effects are nausea, kidney and liver problems, low white blood counts, and vomiting.
Targeted drugs
Targeted therapy drugs are newer treatments that may be used for certain types of GI neuroendocrine tumors. These drugs affect mainly cancer cells , but not normal cells in the body. They may work even if other treatments don’t. They come as pills that you take at home. Side effects from these drugs are different from chemo side effects.
Other drugs
Drugs like octreotide and lanreotide are used to treat the symptoms of carcinoid syndrome and help shrink neuroendocrine tumors. They are given as injections (shots) just under the skin.
Clinical trials
Clinical trials are research studies that test new drugs or other treatments in people. They compare standard treatments with others that might be better.
Clinical trials are one way to get the newest cancer treatment. They often are the best way for doctors to find better ways to treat cancer. If your doctor can find one that’s studying the kind of cancer you have, it’s up to you whether to take part. And if you do sign up for a clinical trial, you can always stop at any time.
If you would like to learn more about clinical trials that might be right for you, start by asking your doctor if your clinic or hospital conducts clinical trials. See Clinical Trials to learn more.
What about other treatments that I hear about?
When you have cancer, you might hear about other ways to treat your cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, diets, or other things.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown to not be helpful. A few have even been found to be harmful. You might feel you want to know more about these treatments. Talk to your doctor about anything you are thinking about using, whether it’s a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Questions to ask the doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- What is the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, what will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too?
- What’s the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- What’s the next step?
What will happen after treatment?
You’ll be glad when treatment is over. However, it’s hard not to worry about cancer coming back. Even when cancer never comes back, people still worry about this.
For years after treatment ends, you will see your cancer doctor. Be sure to go to all follow-up visits. You will have exams, blood tests, and maybe other tests like CT scans or octreotide scans, to see if the cancer has come back.
For the first year after treatment, your visits may be every 6 months. You may have CT scans and blood tests. After the first few years, your visits might be every 6 to 12 months. After 5 years, they may be once a year.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about ways to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You can’t change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life – making healthy choices and feeling as well as you can.
Anyone with cancer, their caregivers, families, and friends, can benefit from help and support. The American Cancer Society offers the Cancer Survivors Network (CSN), a safe place to connect with others who share similar interests and experiences. We also partner with CaringBridge, a free online tool that helps people dealing with illnesses like cancer stay in touch with their friends, family members, and support network by creating their own personal page where they share their journey and health updates.
- Written by
- Words to know
- How can I learn more?

Developed by the American Cancer Society medical and editorial content team with medical review and contribution by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Biopsy (BY-op-see): Taking out small pieces of an abnormal area to see if there are cancer cells in it.
Gastroenterologist (GAS-tro-EN-ter-AHL-uh-jist): A doctor who treats diseases of the digestive system. Also called a GI doctor.
Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: The long pathway inside the body through which food passes. It includes hollow organs such as the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine (colon and rectum). Also called the digestive tract.
Metastasis (muh-TAS-tuh-sis): Cancer cells that have spread from where they started to other places in the body.
We have a lot more information for you. You can find it online at www.cancer.org. Or, you can call our toll-free number at 1-800-227-2345 to talk to one of our cancer information specialists.
Last Revised: August 8, 2025
American Cancer Society medical information is copyrighted material. For reprint requests, please see our Content Usage Policy.
American Cancer Society Emails
Sign up to stay up-to-date with news, valuable information, and ways to get involved with the American Cancer Society.



